Understanding Topographic Surveys: What Is a Topographic Survey?
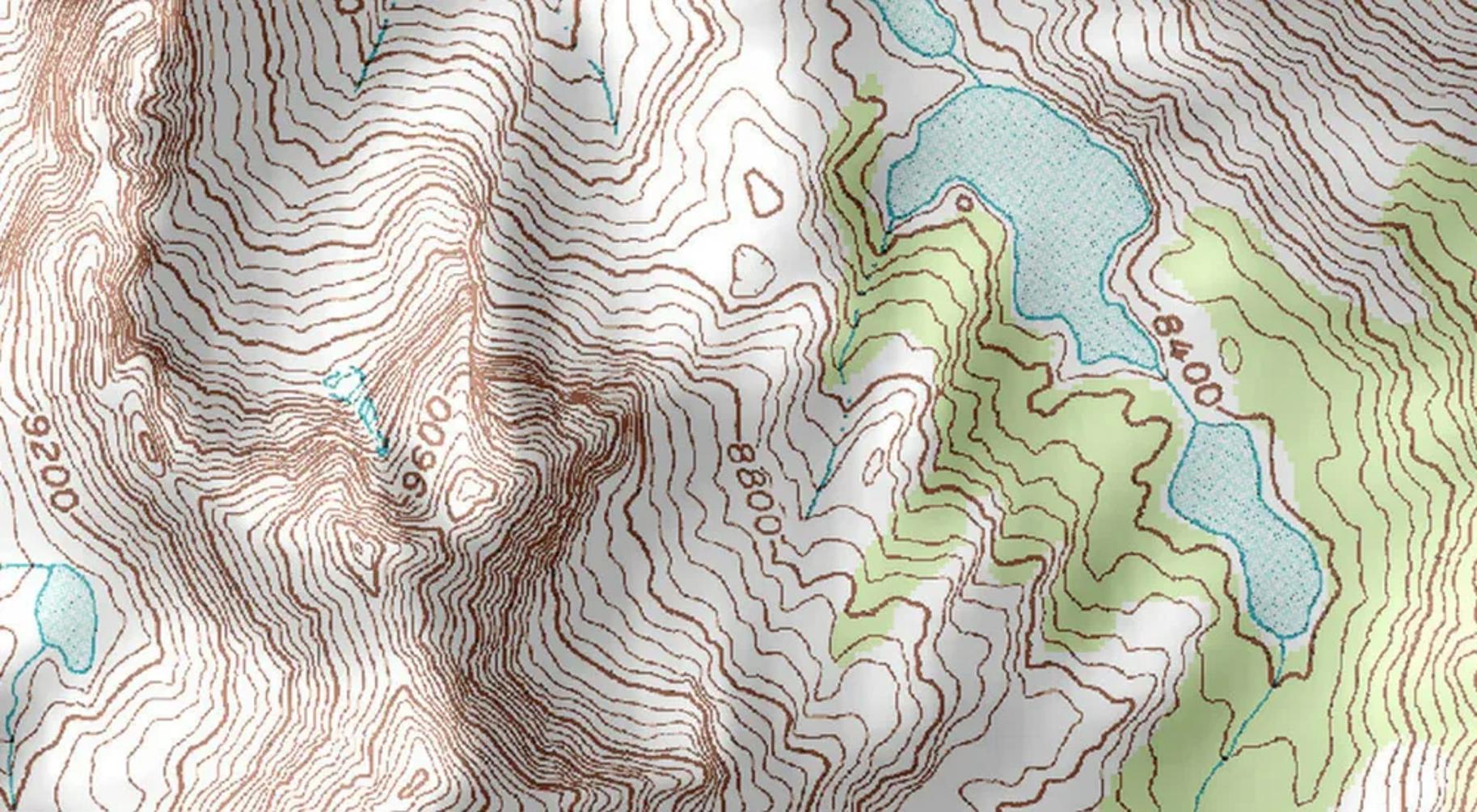
Understanding Topographic Surveys: What Is a Topographic Survey?
Key Takeaways
A topographic survey provides a detailed representation of land features, essential for informed planning and development in construction and urban projects.
Key components of topographic surveys include contour lines, natural features, and man-made structures, all of which are vital for a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
Modern topographic surveys utilize advanced tools like GPS and photogrammetry, improving accuracy and efficiency in data collection and analysis.
Definition of a Topographic Survey

A topographic survey is a detailed and precise representation of a specific area of land, showcasing its natural and human-made features. These surveys are essential tools in the visualization and development of land, providing crucial information on elevation levels and landforms. With the help of topographic surveys, architects and engineers can better understand the layout of a site, allowing them to design structures that are well-suited to the terrain and avoid potential issues that could arise from improper planning.
Topographic surveys provide a comprehensive view of the land, including the locations of natural features like rivers, trees, and hills, as well as man-made structures such as roads, buildings, and utility lines. This information is invaluable for professionals involved in construction, urban planning, land surveys, and environmental management, as it ensures that every aspect of the land is taken into account during the planning and development stages.
Topographic surveys offer a clear picture of the land’s characteristics, helping to prevent costly mistakes and ensure efficient and effective project completion.
Key Components of Topographic Surveys
Topographic surveys are composed of several key components that provide a detailed understanding of the surveyed area. These components include contour lines, natural features, and man-made features. Each element plays a vital role in creating a comprehensive topographic map that accurately represents the terrain and its attributes.
The following subsections delve deeper into these components, highlighting their significance and their contribution to the overall accuracy and usefulness of topographic surveys.
Contour Lines
Contour lines are the backbone of any topographic survey, representing the changes in elevation across the land. These lines connect points of equal height, creating a visual representation of the terrain’s ups and downs. Examining the spacing and patterns of contour lines allows for easy identification of features such as peaks, valleys, and slopes, which are crucial for understanding the topography of a surveyed area. For instance, closely spaced contour lines indicate steep terrain, while widely spaced lines suggest a gentler slope.
The importance of contour lines cannot be overstated, as they provide a clear and detailed picture of elevation changes that are essential for various applications, from construction projects to environmental management.
Contour lines illustrate the terrain’s vertical angles and horizontal distances, aiding surveyors and planners in making informed decisions about land use and development. This simple geometry yet powerful tool has been a cornerstone of topographic mapping since the days of prehistoric surveyors, continuing to play a critical role in modern land surveying and boundary lines.
Natural Features
Natural features are another crucial component of topographic surveys, encompassing elements such as vegetation, bodies of water, and geological formations. These features provide valuable insights into the land’s characteristics, helping civil engineers and architects design projects that harmonize with the natural environment. For instance, understanding the location and type of vegetation can inform decisions about landscaping and erosion control, while mapping water bodies like rivers and lakes can influence drainage and flood prevention measures.
Topographic surveys also play a significant role in environmental protection by identifying and documenting natural features that require conservation in history. This information is essential for urban planners who need to balance development with the preservation of natural habitats and resources, as these surveys fulfill their primary roles.
Incorporating natural features into designs allows planners to create sustainable and resilient infrastructure that respects and enhances the existing landscape. Thus, topographic surveys serve as a vital tool for promoting responsible land use and environmental stewardship.
Man-Made Features
In addition to natural features, topographic surveys also document man-made structures such as roads, buildings, and utility installations. These human-made elements are integral to creating a comprehensive map of the surveyed area, as they provide essential information for construction and land development planning.
Identifying the location and layout of existing infrastructure through topographic surveys and as built survey ensures new projects integrate seamlessly with the surrounding environment and comply with relevant regulations.
Tools and Techniques Used in Topographic Surveys
Modern topographic surveys rely on a range of advanced tools and techniques to gather precise and accurate data about the land. These tools include GPS systems, total stations, and electronic distance measurement devices, among others. By utilizing state-of-the-art technology, professional land surveyors can create highly detailed topographic maps that accurately represent the surveyed area.
The following subsections explore commonly used tools and techniques in topographic surveying, highlighting their capabilities and their contribution to the overall accuracy of the surveys.
Total Stations and GPS
Total stations are versatile instruments that integrate electronic distance measurement with theodolite capabilities to provide precise site data collection. These devices measure distances and angles, allowing surveyors to gather accurate information about the land’s topography efficiently. Combining these functions allows a total station to enable surveyors to calculate precise coordinates for each point and ensure consistency in elevation data, including the total length of surveyed lines. Additionally, total stations can measure angles.
GPS systems are another essential tool in modern topographic surveying, offering high accuracy and ease of use. GPS technology allows surveyors to quickly and accurately determine the position of various points on the land, crucial for creating detailed topographic maps.
The integration of total stations and GPS systems enhances the precision and reliability of topographic surveys, ensuring that the data collected is both comprehensive and accurate.
Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)
Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM) technology is vital for accurately measuring long distances in topographic surveys. Calculating the time it takes for a signal to travel to an object and return allows EDM devices to provide precise elevation measurements, critical for creating accurate topographic maps.
This technology improves the efficiency and accuracy of surveying tasks, leading to better project outcomes and more reliable accurate measurements data.
Satellite Imagery and Photogrammetry Software
Satellite imagery and photogrammetry software have revolutionized the field of topographic surveying by enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of data collection and analysis. These tools allow surveyors to capture detailed images of the land from aerial or satellite perspectives, which can then be processed to create highly accurate topographic maps and 3D models. The use of satellite imagery ensures that surveyors can cover large areas quickly and accurately, while photogrammetry software translates raw data into usable formats for further analysis and mapping.
Integrating satellite imagery and photogrammetry software enables modern topographic surveys to provide a level of detail and precision that was previously unattainable. This combination of advanced technology and traditional surveying techniques enables surveyors to produce comprehensive and reliable topographic maps that meet the needs of various industries, from construction to environmental management.
Applications of Topographic Surveys

Topographic surveys have a wide range of applications across different fields, providing essential data for land development, construction, urban planning, and land management. These surveys help professionals visualize and design projects by displaying both natural and artificial features of the land.
The following subsections explore key applications of topographic surveys, highlighting their importance in construction projects, urban planning, and land management.
Construction Projects
Topographic surveys play a crucial role in planning and executing construction projects by providing essential information about the landscape and elevation changes that must be considered. These surveys help construction professionals understand the property’s layout and create designs that accommodate elevation or landscape changes, ensuring that structures are built on stable ground and comply with relevant regulations. For instance, identifying the location of existing infrastructure and utilities is vital for planning construction and avoiding potential conflicts during the building process.
Documenting man-made features such as roads, bridges, and utility lines through topographic surveys provides a comprehensive overview of the site, allowing for better planning and execution of construction projects. This information is crucial for civil engineers and architects, who rely on accurate topographic data to design safe and efficient structures that integrate seamlessly with the surrounding environment, including aspects of civil engineering.
Urban Planning
In urban planning, topographic surveys are indispensable tools for designing city infrastructure and ensuring effective land use and zoning compliance. These surveys support urban planners in creating efficient transportation systems and infrastructure layouts by providing detailed information about the natural and man-made features of the land. For example, understanding the location of rivers, lakes, and forested areas can help planners design sustainable and resilient urban environments that balance development with environmental preservation.
Topographic surveys also play a crucial role in identifying wildlife habitats and other natural features that may impact land use planning. Incorporating this information into their designs allows urban planners to create vibrant and livable cities that respect and enhance the natural landscape. This holistic approach to urban planning ensures that cities are built in harmony with their surroundings, promoting sustainable development and environmental stewardship.
Land Management
Topographic surveys are essential for effective land management, as they provide accurate data for zoning decisions and optimizing land use. Offering detailed insights into the terrain and natural features of a specific location, these surveys help land managers assess the suitability of land for various purposes, such as residential, commercial, or recreational development. This information is crucial for making informed decisions that ensure compliance with environmental regulations and optimize land resources.
In addition to zoning and land use planning, topographic surveys assist in resolving real property boundary disputes by providing accurate legal descriptions and identifying legal boundaries. This boundary survey helps prevent conflicts and ensures that land is managed effectively and responsibly.
Furthermore, topographic surveys can identify flood-prone areas, which is vital for disaster prevention and effective land management.
Conducting a Topographic Survey

Conducting a topographic survey involves a series of steps, from fieldwork to data processing and final mapping. The process begins with on-site measurements to gather detailed elevation and spatial information, followed by the use of advanced tools to ensure precise data collection.
Once the data is collected, it undergoes post-processing to create accurate and detailed topographic maps that can be used for various applications. In the following subsections, we will explore each step of the process in greater detail, highlighting the importance of data collection, post-processing, and final mapping.
Data Collection
The data collection phase of a topographic survey is critical for gathering accurate and detailed information about the land’s elevation and spatial characteristics. Surveyors use advanced tools such as electromagnetic distance measuring (EDM) devices, which calculate the time it takes for a signal to travel to an object and return, ensuring precise measurements over long distances. These measurements are essential for creating accurate topographic maps that reflect the true nature of the terrain.
To ensure the accuracy of the data collected, surveyors establish control points with known coordinates across the surveyed area. These control points serve as reference points for all subsequent measurements, allowing surveyors to verify the consistency and reliability of the data. By combining advanced technology with meticulous fieldwork, surveyors can gather the information needed to create comprehensive and accurate topographic surveys.
Post Processing
Post-processing is a crucial step in topographic surveying, where raw data collected during the fieldwork is transformed into usable maps and models. Photogrammetry software plays a key role in this process, allowing surveyors to create detailed maps from images captured via satellite or aerial methods, utilizing image processing techniques.
By integrating these images with other survey data, the software produces accurate 3D models and topographic maps that can be used to build various applications. This step ensures that the final outputs are precise and reliable, providing a solid foundation for land development and management.
Final Mapping
The final mapping phase of a topographic survey involves creating a detailed map that outlines the terrain, elevation changes, and property structures within the surveyed area. This map serves as a comprehensive representation of the land, providing valuable insights for architects, engineers, and land managers. The data analysis performed during post-processing is essential for ensuring that the map accurately reflects the land’s characteristics and is suitable for its intended use.
In addition to providing detailed topographic information, the final map includes contour lines, natural features, and man-made structures, offering a complete picture of the surveyed area. This comprehensive map is indispensable for various applications, from planning construction projects to managing land resources effectively, as it is based on the great trigonometrical survey and the datum. For further information, please refer to the accompanying documentation.
Transforming raw survey data into an accurate and detailed map ensures that stakeholders have the information needed to make informed decisions about land use and development.
Choosing a Professional Land Surveyor
Selecting a professional land surveyor is a critical step in ensuring the success of any topographic survey. Choose a surveyor who specializes in topographic surveys relevant to your land development area. A licensed land surveyor recognized by local or national authorities will ensure compliance with industry regulations and provide reliable and accurate results. Evaluating a surveyor’s past projects and portfolio can offer valuable insights into their skill and experience level.
Strong communication skills and responsive customer service are also essential traits to look for in a surveyor. A surveyor who can effectively communicate and address your concerns will help ensure a smooth and efficient surveying process.
Choosing a professional land surveyor with the right expertise and credentials ensures your topographic survey and land survey will be conducted accurately and efficiently, providing essential data for successful land development and management by land developers.
Summary
Topographic surveys are indispensable tools in the fields of construction, urban planning, and land management. They provide detailed and accurate maps of the land, showcasing both natural and man-made features, as well as elevation changes that are crucial for successful land development. By understanding the key components of topographic surveys, such as contour lines, natural features, and man-made structures, stakeholders can make informed decisions that ensure the efficient and sustainable use of land.
The advanced tools and techniques used in modern topographic surveys, including total stations, GPS, EDM, satellite imagery, and photogrammetry software, enhance the accuracy and reliability of the data collected. These surveys have a wide range of applications, from planning construction projects to optimizing land use and ensuring effective urban planning. By choosing a professional and licensed land surveyor, you can be confident that your topographic survey will be conducted with precision and expertise, providing you with the essential data needed for successful land development and management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a topographic survey?
A topographic survey is a detailed representation of land that highlights both natural and human-made features, essential for visualization and development efforts. This precision allows for informed decision-making in land use and construction.
Why are contour lines important in topographic surveys?
Contour lines are crucial in topographic surveys as they illustrate elevation changes and depict the terrain's features, such as peaks and valleys, enabling effective analysis and planning.
What tools are commonly used in topographic surveys?
Topographic surveys commonly utilize tools such as total stations, GPS systems, electronic distance measurement devices, satellite imagery, and photogrammetry software. These instruments are essential for accurate data collection and analysis in the surveying process.
How do topographic surveys assist in construction projects?
Topographic surveys are crucial for construction projects as they offer vital data on landscape and elevation changes, enabling professionals to design structures that align with the terrain and adhere to regulations. This ensures that projects are executed efficiently and effectively.
What should I consider when choosing a professional land surveyor?
When selecting a professional land surveyor, it is essential to evaluate their specialization, licensing, previous project experience, and ability to communicate effectively. These factors will ensure you receive reliable and skilled surveying services.



